or
How to recognize the Subject and Objects in a Georgian sentence?!
For any learner of the Georgian language, the correct use/recognizing of the subject and the objects in a Georgian sentence poses a challenge for a long time. Well, even correctly using/recognizing the right mood and tense of a verb is no simple matter, either.
Take these three examples in aorist indicative: ბიჭმა დაწერა წერილი დედისთვის, ბიჭმა დაუწერა წერილი დედას and წერილი დაიწერა ბიჭის მიერ დედისთვის. The semantic subject can obviously sometimes be in ergative (ბიჭმა) or referred to in a preposition (ბიჭის მიერ). The direct object can be in dative (წერილს) in one sentence and in nominative (წერილი) in another. The indirect object can be in dative (დედას) or in a preposition (დედისთვის). When to use what? Or how to recognize subject, direct object and indirect object?
Today I want to provide you with a hopefully concisive overview on how to do this for verbs of all three conjugation classes. You can already note that in Class I, marking of subject and object varies quite a bit across the moods and tenses, sometimes the subject is in nominative, sometimes in ergative and sometimes in dative; for the objects this is equally complex. The good new is, in verbs of Class-II and Class-III the marking pattern is consistent across all moods and tenses, albeit different between the two classes.
Note that in all verb classes I-III the indirect object can be expressed as a preposition with -ისთვის: დედისთვის - for mother, or using the dative: დედას - for mother; it is just that the dative is not always used (but people would probably understand what you mean).
Here it goes:
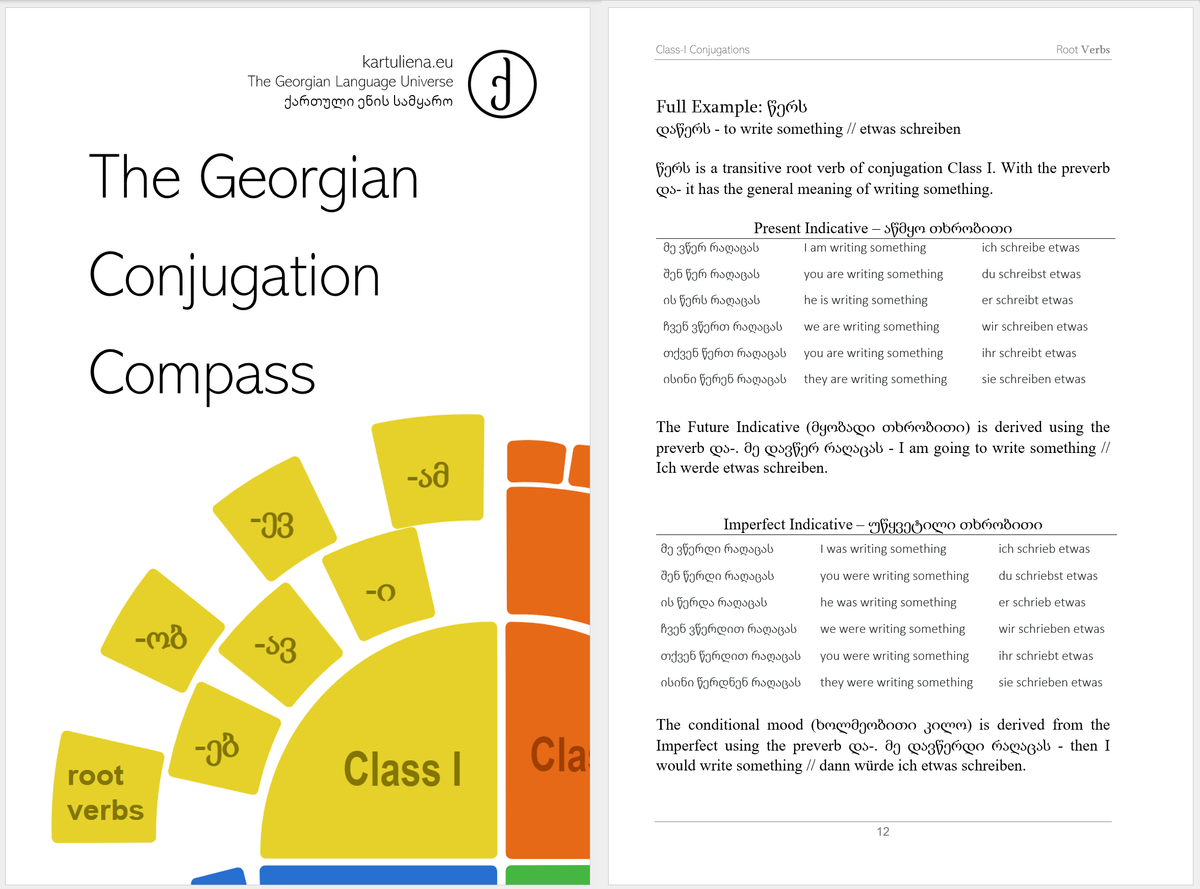
Quick reference for the Class-I Verbs:
| Moods & Tenses | Subject | Verb | Direct Object | Indirect Object |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present Group* | Nominative | - | Dative | Dative or preposition + -ისთვის |
| Aorist, Optative | Ergative | - | Nominative | Dative or preposition + -ისთვის |
| Perfect, PluPerfect | Dative | - | Nominative | Dative or preposition + -ისთვის |
*Note that the Present Group includes all Present Indicative, Future Indicative, Imperfect Indicative, Conditional Mood and the Subjunctive Mood.
Example:
Present Indicative
| Subject | Verb | Direct Object | Indirect Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | - | Dative | preposition + -ისთვის |
| ბიჭი | წერს | წერილს | დედისთვის |
| the boy | writes | a letter | for mother |
When using the verb with the indirect object marker უ-, the indirect object is marked in dative.
Present Indicative
| Subject | Verb | Direct Object | Indirect Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | - | Dative | Dative |
| ბიჭი | უწერს | წერილს | დედას |
| the boy | writes (for) | a letter | for mother |
Dive deeper and find more details on this and more examples with subjects and objects from sentences in the imperfect, subjunctive, aorist, optative, perfect and more on this page here linked below ...
Quick reference for the Class-II Verbs:
Due to their often being of passive nature, it is not easy keeping track of syntactic subjects, objects or semantic agents and patients in theses sentences. But see, how the pattern is the same across all moods and tenses? What a relief!
| Moods & Tenses | Prepositional Object (Agent) |
Verb | Subject (Patient) |
Indirect Object (Recipient) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present Group* | genitive + მიერ | - | Nominative | Dative or preposition + -ისთვის |
| Aorist, Optative | genitive + მიერ | - | Nominative | Dative or preposition + -ისთვის |
| Perfect, PluPerfect | genitive + მიერ | - | Nominative | Dative or preposition + -ისთვის |
Examples:
Present Indicative
| Prepositional Object (Agent) |
Verb | Subject (Patient) |
Indirect Object (Recipient) |
|---|---|---|---|
| genitive + მიერ | - | Dative | preposition + -ისთვის |
| ბიჭის მიერ | იწერება | წერილი | დედისთვის |
| by the boy | is written | the letter | for mother |
Aorist Indicative
| Prepositional Object (Agent) |
Verb | Subject (Patient) |
Indirect Object (Recipient) |
|---|---|---|---|
| genitive + მიერ | - | Dative | preposition + -ისთვის |
| ბიჭის მიერ | დაიწერა | წერილი | დედისთვის |
| by the boy | was written | the letter | for mother |
Again, more details and lots of example sentences are on this separate page:

Quick reference for the Class-III Verbs:
Again, the same marking of subject and objects across the board!
| Moods & Tenses | Subject | Verb | Direct Object | Indirect Object |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present Group* | Dative | - | Nominative | preposition + -ისთვის |
| Aorist, Optative | Dative | - | Nominative | preposition + -ისთვის |
| Perfect, PluPerfect | Dative | - | Nominative | preposition + -ისთვის |
Examples:
Present Indicative
| Subject | Verb | Direct Object | Indirect Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dative | - | Nominative | preposition + -ისთვის |
| მამას | მოსწონს | კატა | ბავშვისთვის |
| the father | likes | the cat | for the child |
Aorist Indicative
| Subject | Verb | Direct Object | Indirect Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dative | - | Nominative | preposition + -ისთვის |
| მამას | მოეწონა | კატა | ბავშვისთვის |
| the father | liked | the cat | for the child |
Perfect Indicative
| Subject | Verb | Direct Object | Indirect Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dative | - | Nominative | preposition + -ისთვის |
| მამას | მოსწონებია | კატა | ბავშვისთვის |
| the father | has liked | the cat | for the child |
Again, here is the link to the page with more details:

Enjoy! გაამოთ!
P. S. I am steadily working on the pages of kartuliena.eu – behind the scenes – The blog updates merely summarize the "completion" of certain parts/chapters and milestones reached. The real treasure is in the hundreds of pages to explore and use as a regular study companion! Check this page here to see what is new each week:

